What is Cannabis?
Basics
Cannabis
Cannabis, also known as marijuana, weed, or pot, generally refers to the dried leaves, flowers, stems, and seeds from the cannabis plant (plant family Cannabaceae). Typical cannabis plants contain hundreds of compounds, including the most known: cannabinoids and terpenes.
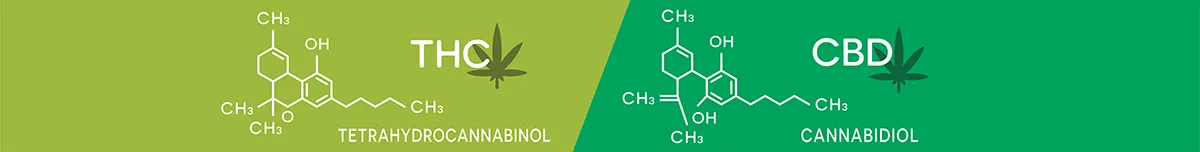
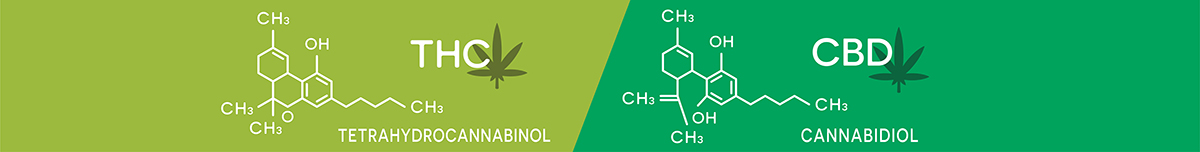
- THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) – The intoxicating compound, responsible for creating the feeling of being “high.”
- CBD (cannabidiol) – One of the two main compounds, usually derived from the hemp plant. Hemp is the same plant as cannabis, but specific strains are grown to meet the current legal definition of having less than 0.3% THC.
- Terpenes – Naturally occurring, highly aromatic compounds that determine the smell of many plants and herbs and contribute to their flavor. Terpenes make certain cannabis strains smell or taste different from others, and when combined with THC, can affect how cannabis makes you feel.
- Flavonoids – Groups of compounds found in foods and plants. These affect the taste and smell of cannabis and may contribute to antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Other cannabinoids – These come from trichomes (resin glands) found on the plant’s buds, flowers, and leaves. The effects of these cannabinoids are less well known and continue to be studied. There are an estimated 100 to 200 different cannabinoids.
Other Common Terms:
- Cannabis cultivars (commonly called strains)
The various unique cannabinoid and terpene combinations found in cannabis plants.
- “Indica” and “Sativa”
The interbreeding/hybridization of cannabis has made the terms indica and sativa very subjective. It is the complete cannabinoid and terpene profile that a consumer should consider when looking for desired potential effects.
- Endocannabinoid system
A network of chemical signals and cellular receptors throughout the human body that help regulate the central nervous and other systems. Both THC and CBD can act on the cannabinoid receptors all over the body but with different effects.
- Endocannabinoids
Cannabinoids produced by the body.
- Phytocannabinoids
Cannabinoids produced by the cannabis plant.
- Synthetic cannabinoids
Chemically produced cannabinoids that are not sourced from the cannabis plant. Primarily known as K2, Spice, Bath Salts, and synthetic marijuana, these products can be unpredictable, harmful, and potentially life-threatening. They are illegal in Washington State.
Note: This description applies to non-medical use. The FDA approved specific medications that are synthetic or semi-synthetic cannabinoids, namely dronabinol and nabilone, available by prescription at a pharmacy.
- The “Entourage Effect”
This theory is that by combining THC with other cannabis compounds, i.e., CBD and terpenes, there is a modulating effect. More research is needed to better understand the combinations and levels that will produce the desired effects.
- Hemp
The same plant as cannabis but specific cultivars (strains) that are grown to meet a legal definition of having less than 0.3% THC on a “dry weight” basis. Hemp is used to make a variety of commercial and industrial products, including rope, textiles, clothing, shoes, food, paper, bioplastics, insulation, and biofuel. Information about the WA State hemp program is found on the Department of Agriculture website.